There are several sources for ephemeris data for comets, asteroids, small bodies, and interplanetary spacecraft. In most cases the data formats are SPICE files or a custom ephemeris format.
Click these to jump to a section in this FAQ:
Downloading the DataLoading the data into STK
Downloading the data
There are a number of data sources; the more popular ones are listed here:
JPL Horizons Ephemeris Importer UI Plugin
A UI Plugin is available for STK 12 to query the JPL Horizons API and load it into STK automatically. The plugin is at AGI's Github, and you can get the instructions to deploy the plugin here. No administrator privileges are required.
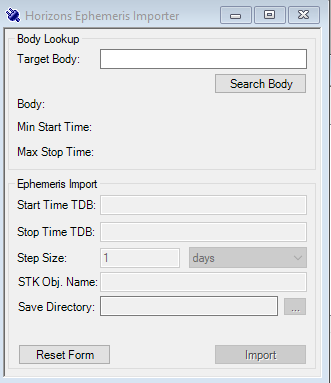
JPL Horizons web interface
You can generate an ephemeris file from the JPL Horizons web interface and then load that into STK. Since it is in a custom format, you will need an ephemeris reader to load the data into STK.
1. Go to the
JPL Horizons web interface and use the following settings:
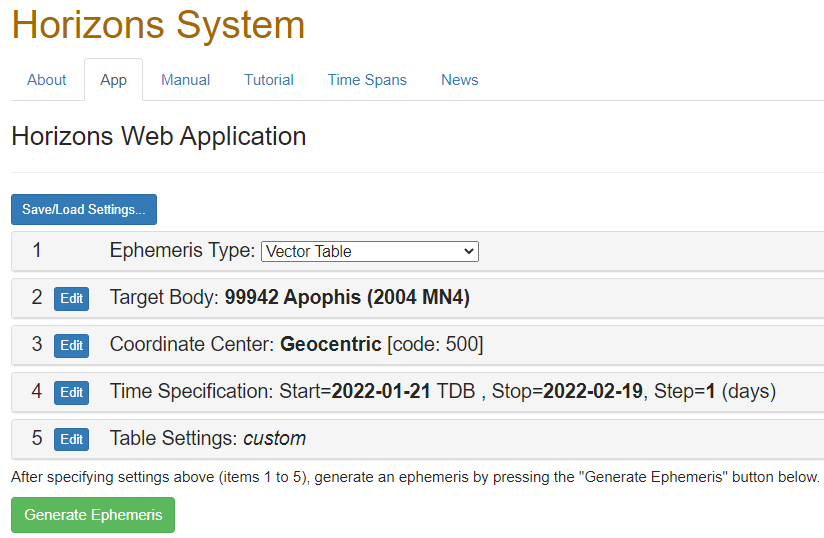
2. Use the following table settings:
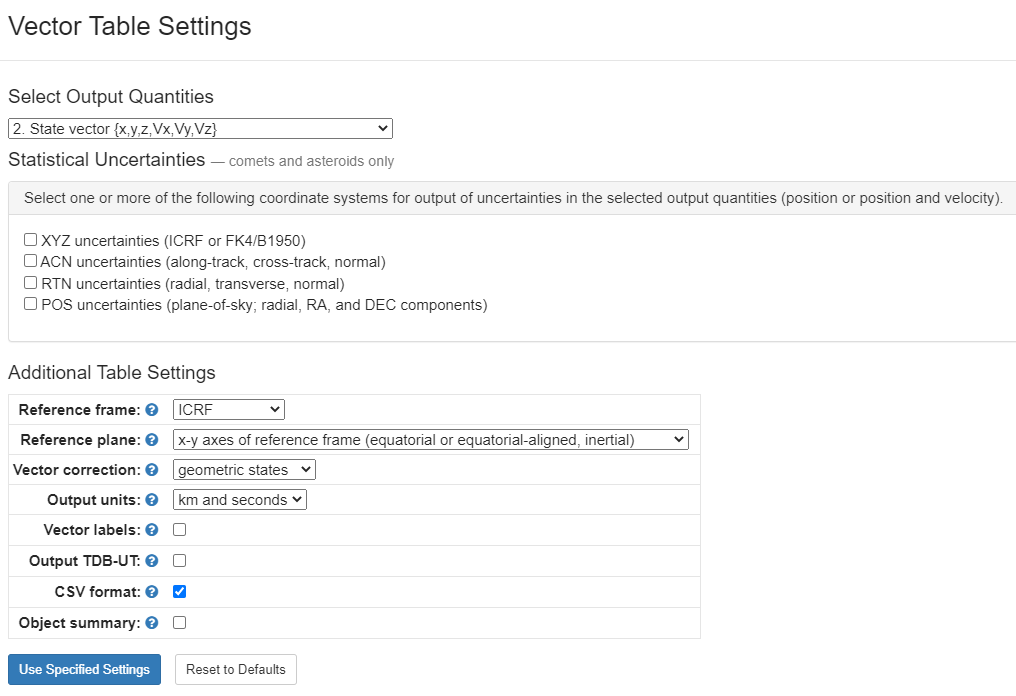
3. Save the resulting output as a TXT file.
JPL Horizons email interface
Instead of selecting the desired settings in the Horizons web interface (see above), you can send an email with correctly formatted instructions to
horizons@ssd.jpl.nasa.gov and receive the same ephemeris results by email. You will need to register the
same ephemeris reader to get the data into STK. For more information, email
horizons@ssd.jpl.nasa.gov with BATCH-LONG as the subject to receive an email containing detailed instructions. To get the properly formatted ephemeris results, send an email containing JOB as the subject and the body containing something like this:
!$$SOF
EMAIL_ADDR = ' '
COMMAND = '101955'
OBJ_DATA = 'YES'
MAKE_EPHEM = 'YES'
EPHEM_TYPE = 'VEC'
CENTER = 'Geocentric'
START_TIME = '2021-JUN-9 00:00'
STOP_TIME = '2021-JUL-9 00:00'
STEP_SIZE = '60 min'
REF_PLANE= 'FRAME'
REF_SYSTEM = ICRF
OUT_UNITS = 'KM-S'
VEC_TABLE = '2'
ANG_FORMAT = 'DEG'
TIME_ZONE = '+00:00'
TIME_DIGITS = 'SEC'
RANGE_UNITS = 'KM'
CSV_FORMAT = 'YES'
!$$EOF
JPL Horizons telnet interface
The JPL Horizons telnet interface enables you to download SPICE files, which you can then load into STK.
Using the Horizons system1. Open a telnet connection with the URL horizons.jpl.nasa.gov over port 6775, using the method of your choice.
A DOS prompt will appear showing the following:
JPL Horizons, vers SUN-v3.32b
Type `?' for brief intro, `?!' for more details
System news updated Nov 13, 2007
Horizons>
2. At the prompt, type the common name, small space body designation name, or SPICE ID number at the prompt. For example:
Horizons> 2004 MN4
The following response will appear:
>>EXACT<< designation search [CASE & SPACE sensitive]:
DES = 2004 MN4;
Continue [ =yes, n=no, ? ] :
3. Press the Enter key to search for the body.
The search results should be similar to the following:
*******************************************************************************
JPL/HORIZONS 99942 Apophis (2004 MN4) 2007-Dec-11 08:09:00
Rec #: 99942 (+COV) Soln.date: 2006-Sep-01_00:50:35 # obs: 738 (2004-2006)
FK5/J2000.0 helio. ecliptic osc. elements (AU, DAYS, DEG, period=Julian yrs):
EPOCH= 2453442.5 ! 2005-Mar-13.00 (CT) Residual RMS= .30901
EC= .191054853916459 QR= .7461531666439291 TP= 2453600.734981114
OM= 204.4721548004914 W= 126.3839706419199 IN= 3.330920734685656
A= .9223779514054623 MA= 183.94709163245 ADIST= 1.098602736166995
PER= .88587 N= 1.112604224 ANGMOM= .016216656
DAN= 1.0023 DDN= .7982399999999999 L= 330.9024012
B= 2.6810584 TP= 2005-Aug-18.2349811
Physical parameters (KM, SEC, rotational period in hours):
GM= n.a. RAD= .135 ROTPER= n.a.
H= 19.7 G= .250 B-V= n.a.
ALBEDO= .330 STYP= n.a.
ASTEROID comments:
1: soln ref.= JPL#139, PHA OCC=0 radar( 2 delay, 5 Dop.)
2: source=ORB
*******************************************************************************
Select ... [A]pproaches, [E]phemeris, [F]tp,[M]ail,[R]edisplay, [S]PK,?,:
4. STK-compatible SPICE files are created using the "[S]PK" option. Enter
S to create a SPICE file.
Select ... [A]pproaches, [E]phemeris, [F]tp,[M]ail,[R]edisplay, [S]PK,?,: S
The following response will appear:
Assigned SPK object ID: 2099942
Enter your Internet e-mail address [?]:
5. Enter and confirm your e-mail address.
Enter your Internet e-mail address [?]: support@agi.com
"support@agi.com"
Confirm e-mail address [yes(),no] :
The following response will appear.
Address stored this login only ... use "email" cmd to change
SPK text transfer format [ YES, NO, ? ] :
6. Since a binary SPICE file is smaller than its SPK ASCII equivalent, choose that option. Enter
No at this prompt.
SPK text transfer format [ YES, NO, ? ] : No
The following response will appear:
SPK object START [ t >= 1900-Jan-01, ? ] :
7. Type in the Start and Stop times for your SPICE file in the appropriate date format.
SPK object START [ t >= 1900-Jan-01, ? ] : 2008-Jan-01
SPK object STOP [ t <= 2101-Jan-01, ? ] : 2009-Jan-01
A response similar to the following will appear:
Chebyshevs constructed on STANDARD mesh.
Current integration step:
2454829.81537 2008 Dec 29.31537 2.6508021
Binary SPK file created.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
A-posteriori SPK fidelity estimate (rel. to integrator):
Max. error (3 std. dev) Time
------------------------ ------------------------
X: 0.6908704060214330D-04 m 2008-Sep-29 03:00:00.000
Y: 0.8218709696074995D-04 m 2008-Jul-11 03:00:00.000
Z: 0.4723960730105999D-04 m 2008-Jul-11 03:00:00.000
RSS: 0.1173001218411825D-03 m 2008-Sep-29 03:00:00.000
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Add more objects to file [ YES, NO, ? ] :
8. Enter
No when asked if you would like to add objects.
Add more objects to file [ YES, NO, ? ] : No
A response similar to the following will appear:
You have 30 minutes to retrieve the following by anonymous FTP:
Machine name: ssd.jpl.nasa.gov
Directory : cd to "/pub/ssd/"
File name : wld26489.15
File type : BINAR
9. Rename the return file so that it has a .bsp extension.
File name : wld26489.bsp
JPL NAIF
The JPL Navigation and Ancillary Information Facility (NAIF) enables you to download SPICE files for asteroids, comets, and spacecraft.
- Go to https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/naif/.
- Using the navigation bar on the left, select Data.
- Click Operational Flight Projects Kernels and Other Non-archived Project Kernels.
- Click one of the links, such as Outer Planet Missions.
- For the given mission, click the link inside the 'spk' column. This will launch an ftp folder view.
- The ftp folder may contain many BSP files, which are compatible with STK. Some folders may also contain text files, such as 'aareadme.txt', that explain the naming conventions and contents of each BSP file. You should pay careful attention in order to obtain actual spacecraft trajectory SPK files and not planetary ephemeris or other related files.
- Download the desired spacecraft ephemeris files into any directory on your computer.
- To load these into STK, create a satellite using the SPICE propagator and browse to the saved file.
ESA COSMOS
The European Space Agency provides SPICE files for the interplanetary missions they are involved in.
- Go to the ESA SPICE site.
- Under Data, select the mission of interest.
- Download (and unzip if necessary) a SPICE file from SEARCH/ACCESS DATA.
Loading the data into STK
SPICE
There are two ways to load SPICE BSP or SPK files into STK.
- As a Satellite object:
Change the propagator of a satellite to SPICE and browse to the desired file.
- As a Planet object:
- Copy your SPICE file into one of the STK SPICE folders using these instructions.
- Restart STK.
- Using the Component Browser (Utilities > Component Browser > Central Bodies), duplicate a CentralBody. Set the EphemerisData of this copy to JplSpice and specify the SPICE ID as described here.
- Insert a new Planet object and set the Basic > Definition > Central Body to this new CentralBody.
JPL Horizons ephemeris
Loading the JPL Horizons formatted ephemeris file requires that you install the ephemeris reader (attached below) first.
Register the ephemeris reader
- Unzip the attached JplHorizonsEphemeris.zip files.
- Register the plugin using the steps from the "How Do I Register a WSC-type Plugin with STK or ODTK? " FAQ.
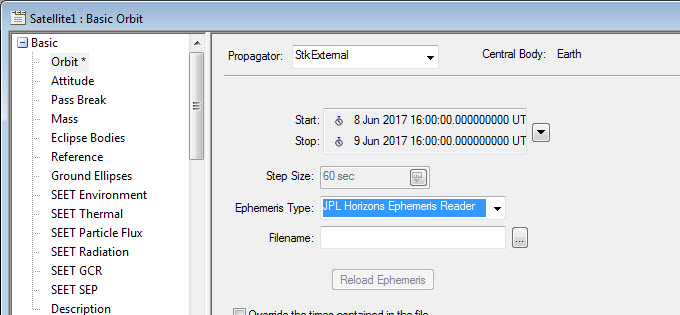
Load ephemeris fileOnce you register the ephemeris reader, proceed as follows:
- Start up STK.
- Create a new scenario.
- Add a satellite. After you change the propagator to StkExternal, you should see the new "JPL Horizons Ephemeris Reader" as an option. You can now load the file you downloaded from the Horizons website.
 Notes
Notes
- Horizons produces vector reports in Julian Data Barycentric Dynamical Time (TDB). Conversion to UTCG occurs when importing the ephemeris into STK, so reports from JPL Horizons in TDB will yield a ~70-second difference from UTCG.
- In Observer reports, Horizons considers an "Apparent" measurement to include the effects of light time delay and aberration, whereas STK defines Apparent as the effects of light time delay only, with Aberration being available as a separate option.
- If you are using osculating orbital elements from the Small Body Database, the coordinate system 'Heliocentric IAU76/J2000 Ecliptic' is equivalent to the 'MeanEclpJ2000' axes within STK. Additionally, the 'node' parameter in the database refers to RAAN in STK, not the Longitude of the Ascending Node.
